
Commercial Range Installation: What You Need to Know
Share
The Foundation of Your Commercial Kitchen: Commercial Range Installation
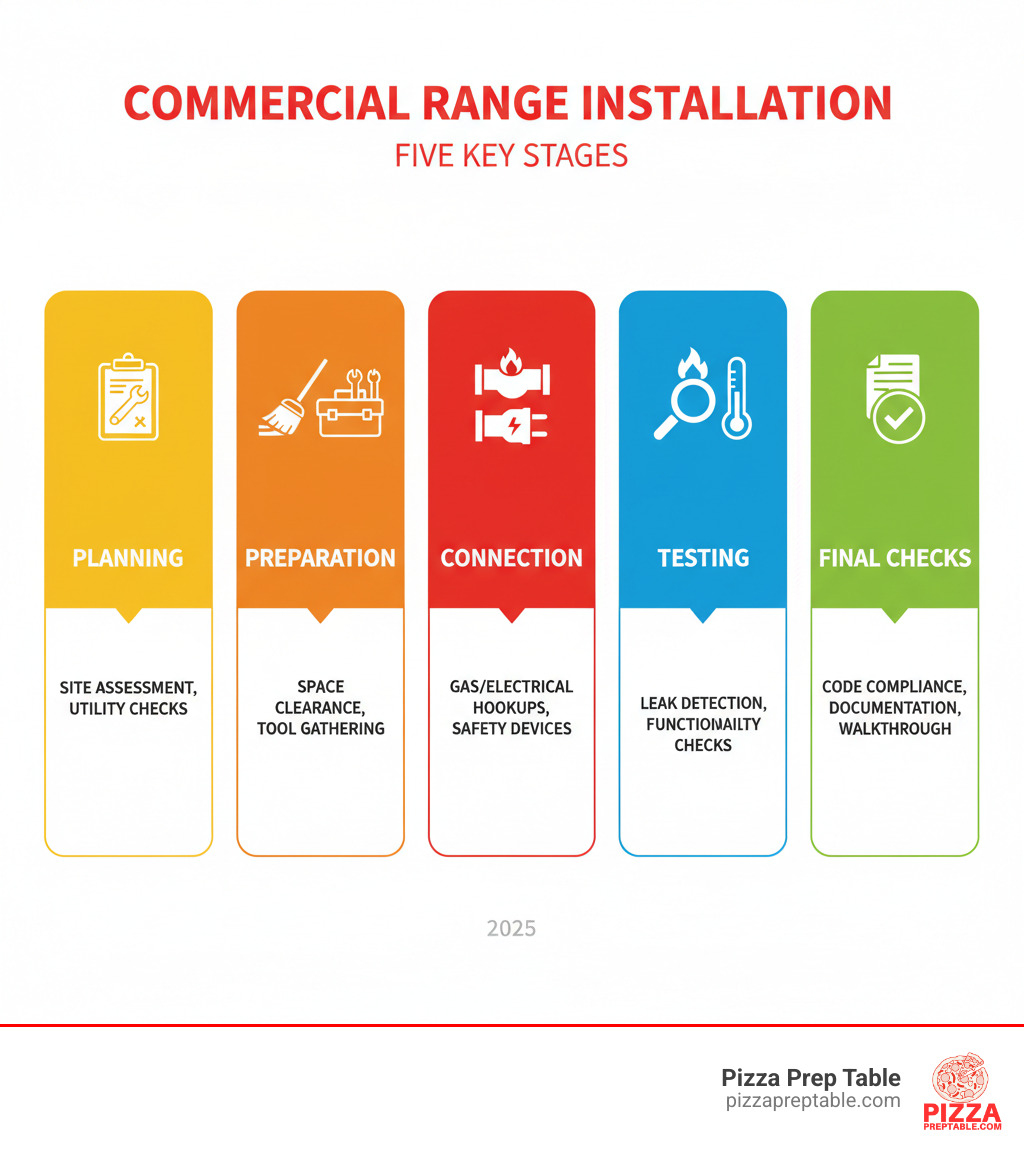
A successful Commercial range installation is the backbone of any efficient foodservice operation. If you're looking for a quick overview of the process, here are the essential steps involved:
- Planning: Assess kitchen space, existing utilities (gas, electric, water), and range type.
- Preparation: Ready the installation site, gather necessary tools and supplies, and ensure ventilation requirements are met.
- Connection: Safely hook up gas lines or electrical circuits, and install crucial safety devices like anti-tip brackets.
- Testing: Conduct thorough leak checks for gas lines, verify all electrical connections, and test burner functionality and oven calibration.
- Final Checks: Confirm compliance with all local codes and regulations, ensure proper documentation, and perform a post-installation walkthrough.
You've invested significantly in your new equipment. Now, you need to make sure it's installed properly and optimized for your business. Proper installation isn't just about getting the range to work; it's about ensuring safety, maximizing performance, and extending the lifespan of your critical kitchen asset.
Consider this: improper installation can cost an average of $5,000 in repair costs and potential fines. What's more, 90% of commercial kitchen fires are linked to improper maintenance and installation. Getting it right from the start can minimize downtime by up to 20% and significantly reduce the risk of equipment failure by 30%. Investing in professional installation also means your equipment could last 15% longer.
Understanding these initial steps is vital. As Sean Kearney, my background in sales within the foodservice industry has shown me the critical impact of proper Commercial range installation. I understand that having the right equipment, correctly installed, is crucial for both efficiency and profitability.
For a clearer visual understanding of these stages, take a look at this infographic:
Step 1: Pre-Installation Planning and Preparation
Before your shiny new commercial range even rolls through the door, the most important work happens: planning. I've seen too many rushed installations turn into expensive headaches. Think of it like prepping your mise en place before service – you wouldn't start cooking without everything in place, right?
Let's start with the basics: measuring your kitchen space. We're not just talking about whether the range fits through the door. You need precise measurements for height, width, and depth, plus extra space around the unit for ventilation and maintenance access. A commercial range is the heart of your cooking line, so its placement affects everything else. You want smooth traffic flow between stations, easy access for your cooks, and room for service during busy shifts. If you're redesigning or setting up a new kitchen, our guide on Commercial Kitchen Layout Design walks you through the entire process.
Next up is assessing your utility hookups, and this is where many installations hit their first snag. You need to know exactly where your gas lines, electrical outlets, and water lines are located – and more importantly, what they can handle. For gas ranges, identify whether you have natural gas or propane, and check the line size. For electric ranges, verify the circuit voltage and amperage before you do anything else. Getting this wrong can delay your installation for days or even create serious safety hazards.
When you're choosing the right range type for your operation, think about what you're actually cooking. Many commercial ranges come with specialized surfaces that can transform your menu options. A built-in griddle, for instance, is perfect for breakfast service or high-volume short-order cooking. Our selection of Kitchen Stoves with Griddle shows how versatile these combinations can be. Charbroilers add that smoky, grilled flavor customers love. Each configuration has slightly different installation needs, especially when it comes to ventilation and utility connections.
Ventilation and Hood Requirements
Here's something that surprises a lot of restaurant owners: ventilation is often more complex and expensive than the range itself. But it's absolutely critical. Commercial cooking generates massive amounts of grease-laden vapors, smoke, and heat. Without proper ventilation, you're looking at poor air quality, uncomfortable working conditions, and a dramatically increased fire risk.
The numbers tell the story. Following NFPA 96 standards for ventilation can reduce fire hazards by up to 50%. We're not talking about a simple exhaust fan here. A proper system includes exhaust hoods (Type I for grease-producing equipment or Type II for steam and heat), ductwork, exhaust fans, and often makeup air systems to replace the air being removed. The specific requirements depend on what you're cooking – a charbroiler puts out way more heat and smoke than standard burners – and the BTU output of your equipment.
This is definitely an area where professional installation matters. Companies that specialize in hood installation understand the codes, the airflow calculations, and the inspection requirements. For a complete breakdown of what you need, check out our guide on Restaurant Kitchen Ventilation Requirements. Getting this right the first time saves you from failed inspections and potential shutdowns down the road.
Necessary Tools and Supplies
A professional installer brings their own equipment, but understanding what's involved helps you appreciate why Commercial range installation isn't a weekend DIY project. The tool list alone tells you this is serious work.
For gas connections, you'll need pipe wrenches to secure fittings properly and Teflon tape (the yellow kind, specifically rated for gas) or pipe sealing compound for leak-free connections. A soapy water solution or electronic leak detector is absolutely essential for checking every connection – this isn't optional. For the physical installation, a level ensures your range sits evenly (critical for even cooking and preventing spills), while a drill secures the anti-tip bracket that keeps the unit from tipping forward when oven doors are opened with heavy pots inside.
Electric installations require a multimeter to verify circuits and connections are correct. Moving the unit safely demands an appliance dolly – commercial ranges are incredibly heavy. You'll also need a new flexible metal appliance connector for gas ranges (existing ones can't be reused for safety and code compliance reasons), plus the gas pressure regulator that comes with your range. Installing this regulator isn't optional – skip it and you'll void your warranty.
For electric ranges, you need the appropriate power cord (either 3-prong or 4-prong, depending on your outlet) or hardwiring setup. Don't forget basic hand tools like screwdrivers, pliers, and wire strippers, plus safety gear including gloves, safety glasses, and sturdy footwear.
The most important tool? Your manufacturer's installation manual. Every range model has specific requirements, and some are surprisingly precise. I've seen manuals specify exact torque settings for fittings, like 15 ft./lbs. for certain connections. These details matter for safety and warranty coverage, so treat that manual like your recipe book – follow it exactly. For an example of detailed instructions, you can refer to resources like this installation guide.
Step 2: The Installation Process - Gas vs. Electric
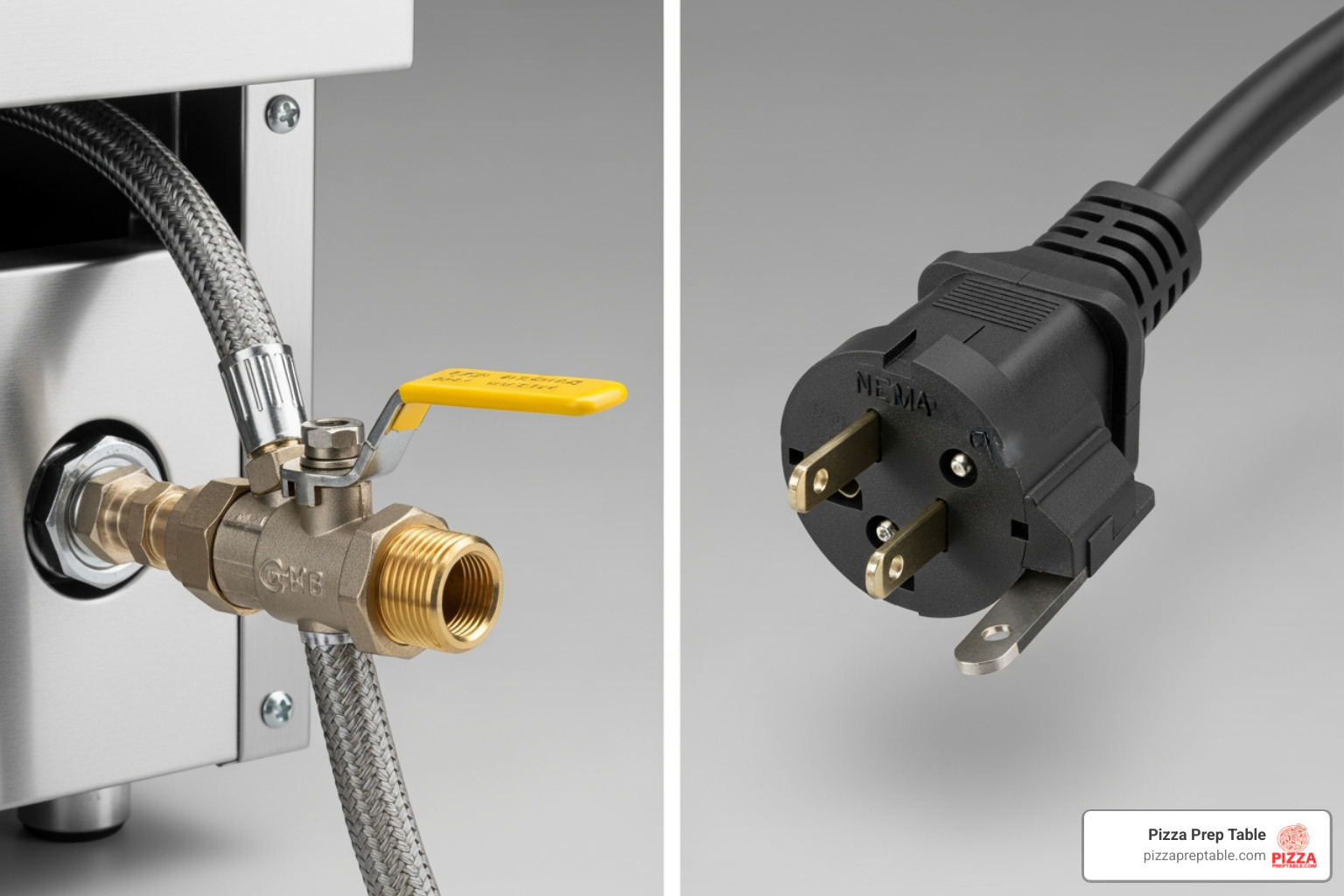
Alright, with all that meticulous planning and preparation behind us, it's finally time for the main event: the actual Commercial range installation! This is where your vision truly comes to life in the kitchen. Whether you're bringing in a powerful gas range or a sleek electric model, the core principles of safety and precision remain paramount. However, the specific steps and considerations differ significantly between the two types, so let's break them down.
Understanding these differences is key to a smooth and compliant installation. Here’s a quick comparison to highlight the main requirements for each:
| Feature | Gas Commercial Range Installation | Electric Commercial Range Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Utility | Natural Gas or Propane (LP). Requires a dedicated gas line. | Dedicated electrical circuit with specific voltage and amperage. |
| Connection Type | Flexible gas connector (always new!), pipe sealant, pressure regulator. | Heavy-duty electrical cord (3-prong or 4-prong) or hardwiring to the circuit. |
| Safety Checks | Soapy water/electronic leak test, proper ventilation, CO detection. | Verify circuit, proper grounding, no exposed wires, functional GFCI (if applicable). |
| Professional Skill | Licensed gas fitter often required. | Licensed electrician often recommended/required. |
For those using gas, understanding the nuances between natural gas and propane can make a big difference in your setup. We've got a great resource explaining this further in our guide on Natural Gas vs Propane.
Essential Steps for a Gas Commercial Range Installation
Installing a gas commercial range involves a sequence of critical steps that demand careful attention. First, the unit needs to be positioned accurately in its designated spot, ensuring it aligns with your kitchen layout and ventilation system. Once in place, leveling the range is absolutely crucial. An unlevel range can lead to uneven cooking, spills, and even premature wear. Use a reliable level and adjust the range's legs until it's perfectly stable.
Next comes the heart of the gas installation: connecting the gas line. This is not a step to take lightly! You must always use a new flexible connector that is approved for commercial use. Never reuse old connectors, as they can degrade and pose serious safety risks. After attaching the connector to both the range and the gas supply line, you'll apply pipe sealant (specifically for gas lines) to all threaded connections to ensure a gas-tight seal. An often-overlooked but vital component is installing the pressure regulator, usually supplied with the range. This device ensures a consistent gas flow and prevents damage to your equipment.
Once all connections are made, the most important safety step is leak testing all connections. You can do this with a simple soapy water solution (look for bubbles!) or an electronic leak detector. If you find any leaks, tighten the connection and retest immediately. Finally, it's time for the moment of truth: lighting and testing burners to ensure they ignite properly and produce a consistent flame. For ranges with ovens, you'll also need to calibrate the oven to guarantee accurate temperature control, which is essential for consistent cooking results.
Key Considerations for Electric Commercial Range Installation
Electric commercial ranges, while not dealing with gas lines, come with their own set of electrical considerations that are just as critical for safety and performance. The first step is to verify the circuit voltage and amperage to ensure it matches the requirements of your new range. Commercial electric ranges often demand significant power, so a dedicated, appropriately rated circuit is a must.
You'll also need to consider the type of electrical outlet: is it a 3-prong vs. 4-prong outlet? This determines the type of power cord required. Some heavy-duty ranges might even require hardwiring requirements, meaning they are directly wired into your electrical system rather than plugging into an outlet. Once the power source is confirmed, connecting the power cord (or hardwiring) must be done precisely, following the manufacturer's instructions.
Crucially, you must ensure proper grounding. This protects against electrical shock and is a non-negotiable safety feature. After all connections are secure, it's time to test all electrical functions. Turn on the range and verify that all heating elements (burners, oven, griddle, etc.) warm up correctly and that all controls are responsive. A quick check of each individual heating element will confirm everything is working as it should, getting your kitchen ready for action!
